
As a part of a project to construct a Rube Goldberg machine, a student wishes to construct a spring-loaded cube launcher. For examples of Rube Goldberg machines, see the beautiful Cog video or the Mythbusters Happy Holidays Rube Machine. Our student plans to trigger the release of the spring with a falling ball. The small cube to be launched has a mass of 119.0 grams. The available spring is a very stiff but light spring that has a spring constant of 461.0 N/m (the spring is so light that it may be considered massless). The spring will be mounted at the bottom of a wooden ramp which makes an angle of 50.0 degrees with the horizontal; the length of the spring is parallel to the ramp with the lower end of the spring fixed in place. For simplicity, assume that the part of the wooden ramp which is underneath the spring is highly polished and very slick; you may assume no friction on the cube by the ramp when the cube is moving on this portion of the ramp. For the rest of the wooden ramp, the coefficients of friction between the ramp surface and the cube surface are 0.590 for static friction and 0.470 for kinetic friction. Measured from the equilibrium position of the free end of the mounted spring, the distance to the top of the ramp is 17.0 cm (this is measured along the ramp) The plan is to compress the spring and maintain the compression with a simple trigger, which will be released by a falling ball. The cube will be at rest on the free end of the compressed spring. When the trigger is released, the spring will expand, shooting the cube up the ramp. The desired speed for the cube when it reaches the top of the ramp (where the cube will leave the ramp as a projectile to continue the Rube Goldberg sequence) is 45.0 cm/s. Your ultimate task will be to calculate the necessary amount of compression for the spring. The Spring is Compressed by 5.90 cm Before attempting the ultimate task, answer the following questions (Parts A-B) for the case in which the spring is compressed by 5.90 cm and then released, shooting the cube up the ramp and into the air.
A) Find the work done on the cube by the spring during the time that the cube is in contact with the spring.
B) What is the speed of the cube at the the instant just before the sliding cube leaves the ramp?

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Physics


Physics, 21.06.2019 19:00, dasiaflowers85
When the velocity of an object is doubled, by what factor is its momentum changed? by what factor is its kinetic energy changed? a) the momentum is zero. b) the momentum is not zero. c) difficult to say.
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:00, chanthonymjones
The cerebellum controls? thirst sensations sleep-wake cycles hand-eye coordination heart rate and pulse
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 16:00, StayPuftMarshadowMan
Frank just graduated from eighth grade. assuming exactly four years from now he will graduate from high school how many seconds does he have until his high school graduation
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
As a part of a project to construct a Rube Goldberg machine, a student wishes to construct a spring-...
Questions in other subjects:

Mathematics, 18.04.2020 07:01

Mathematics, 18.04.2020 07:01

English, 18.04.2020 07:01




Mathematics, 18.04.2020 07:01




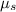 = 0.590
= 0.590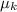 = 0.470
= 0.470 =
= 




