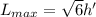Physics, 05.05.2020 00:44, nadia00738
To understand and be able to use the rules for determining allowable orbital angular momentum states.
Several numbers are necessary to describe the states available to an electron in the hydrogen atom. The principal quantum number n determines the energy of the electron. The orbital quantum number l determines the total angular momentum of the electron, and the magnetic quantum number ml determines the component of the angular momentum parallel to a specific axis, usually the z axis.
For a given principal quantum number n, the orbital quantum number can take integer values ranging from zero to n−1. For a given orbital quantum number l, the magnetic quantum number can take integer values from −l to l. A fourth number, the spin ms, is important for interactions with magnetic fields and counting states. The spin can be either +1/2 or −1/2, independent of the values of the other quantum numbers.
The energy of an electron in hydrogen is related to the principal quantum number by En=(−13.60eV)/n^2. The orbital angular momentum is related to the orbital quantum number by L=ℏ√l(l+1), and the orbital angular momentum in the z direction is related to the magnetic quantum number by Lz=mlℏ.
Required:
a. How many different values of I are possible for an electron with principal quantum number n= 5?
b. How many values of mi are possible for an electron with orbital quantum number I= 3?
c. The quantum state of a particle can be specified by giving a complete set of quantum numbers (n, l, mi, ms). How many different quantum states are possible if the principal quantum number is n= 3?
d. Is the state n =3, I =3, m= —2, ms =1/2 an allowable state? If not, why not?
e. What is the maximum angular momentum Lmax that an electron with principal quantum number n= 3 can have?

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 20.06.2019 18:02, 1462264
Consider the orbit of a typical comet around the sun, which is marked at five different positions, s, z, u, x , and p. sun a b x z p s u using kepler's second law of planetary motion, rank those positions in order of their relative speeds, with the position for the fastest speed first.
Answers: 1


Physics, 23.06.2019 08:30, itaheart101
Look at the electroscope, describe how you can cause the two leaves at the bottom to repel each other and stay that way
Answers: 3

Physics, 23.06.2019 09:00, peternice2956
Choose the correct general statement concerning the total potential and kinetic energy at any point along the arc of swing. the total energy at any point along the arc of swing of the pendulum is always less than 12 joules. the total energy at any point along the arc of swing of the pendulum is always more than 12 joules. the total energy at any point along the arc of swing of the pendulum is always equal to 12 joules. not enough information to determine
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
To understand and be able to use the rules for determining allowable orbital angular momentum states...
Questions in other subjects:



Mathematics, 18.03.2021 02:50

Mathematics, 18.03.2021 02:50

Mathematics, 18.03.2021 02:50


Mathematics, 18.03.2021 02:50


Mathematics, 18.03.2021 02:50


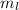 = 7
= 7