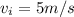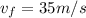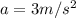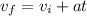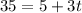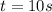s

Physics, 21.03.2020 04:33, ariannawilder0210
An alligator swims to the left with a constant velocity of 5 \,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text s}5
s
m
5, start fraction, start text, m, end text, divided by, start text, s, end text, end fraction. When the alligator sees a bird straight ahead, the alligator speeds up with a constant acceleration of 3 \,\dfrac{\text {m}}{\text s^2}3
s
2
m
3, start fraction, start text, m, end text, divided by, start text, s, end text, squared, end fraction leftward until it reaches a final velocity of 35 \,\dfrac{\text {m}}{\text s}35
s
m
35, start fraction, start text, m, end text, divided by, start text, s, end text, end fraction leftward.
How many seconds does it take the alligator to speed up from 5 \,\dfrac{\text {m}}{\text s}5
s
m
5, start fraction, start text, m, end text, divided by, start text, s, end text, end fraction to 35 \,\dfrac{\text {m}}{\text s}35
s
m
35, start fraction, start text, m, end text, divided by, start text, s, end text, end fraction

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 21.06.2019 19:00, goat46
Prompta snowboarder stands at the top of a hill and decides to see if he can increase his speed on his next trip down the slope. describe one thing the snowboarder could do to incrlase his speed on the slope. explain why this would cause his speed toincrease relate one of newton's laws to this problem.
Answers: 2

Physics, 22.06.2019 07:30, anonymous1813
Some material consisting of a collection of microscopic objects is kept at a high temperature. a photon detector capable of detecting photon energies from infrared through ultraviolet observes photons emitted with energies of 0.3 ev, 0.5 ev, 0.8 ev, 2.0ev, 2.5ev, and 2.8ev. these are the only photon energies observed. (a) draw and label a possible energy-level diagram for one of the microscopic objects, which has four bound states. on the diagram, indicate the transitions corresponding to the emitted photons. explain briefly. (b) would a spring–mass model be a good model for these microscopic objects? why or why not? (c) the material is now cooled down to a very low temperature, and the photon detector stops detecting photon emissions. next, a beam of light with a continuous range of energies from infrared through ultraviolet shines on the material, and the photon detector observes the beam of light after it passes through the material. what photon energies in this beam of light are observed to be significantly reduced in intensity (“dark absorption lines”)? explain briefly.
Answers: 3

Physics, 22.06.2019 17:00, Gabriel134
Two conductors, a and b, are each in the shape of a tetrahedron. but of different sizes. they are charged in the following manner: 1. tetrahedron a is charged from an electrostatic generator to charge q. 2. tetrahedron a is briefly touched to tetrahedron b. 3. steps 1 and 2 are repeated until the charge on tetrahedron b reaches a maximum value. if the charge on tetrahedron b was q/4 after the first time it touched tetrahedron a. what is the final charge qbmax on tetrahedron b?
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
An alligator swims to the left with a constant velocity of 5 \,\dfrac{\text{m}}{\text s}5
s
s
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 28.06.2019 15:00

English, 28.06.2019 15:00


Physics, 28.06.2019 15:00


Health, 28.06.2019 15:00