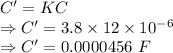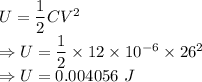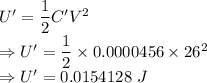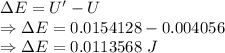A 12.0 μF capacitor is connected to a power supply that keeps a constant potential difference of 26.0 V across the plates. A piece of material having a dielectric constant of 3.80 is placed between the plates, completely filling the space between them.
(a) How much energy is stored in the capacitor before the dielectric is inserted?
(b) How much energy is stored in the capacitor after the dielectric is inserted?
(c) By how much did the energy change during the insertion? Did it increase or1 decrease?
(d) Explain why inserting the dielectric (or equivalently exchanging air with the material) causes a change in the stored energy of the capacitor.

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Physics



Physics, 22.06.2019 14:40, akitchen10
A5 foot by 5 foot box culvert is buried 6 feet beneath the surface of the ground. a crosssection of this very long culvert (into and out of the page) is illustrated below. assume that the soil in which the culvert is buried has the following properties: jt = 120 pcf, w = 12%, ko = 0.50, ka = 0.33, and kp = 3.00. calculate the total horizontal force per unit length of culvert (fh) felt on one of the vertical faces of the culvert.
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 15:30, melanieambrosy
To understand the behavior of the electric field at the surface of a conductor, and its relationship to surface charge on the conductor. a conductor is placed in an external electrostatic field. the external field is uniform before the conductor is placed within it. the conductor is completely isolated from any source of current or charge. part a: which of the following describes the electric field inside this conductor? it is in the same direction as the original external field. it is in the opposite direction from that of the original external field. it has a direction determined entirely by the charge on its surface. it is always zero. part b: the charge density inside the conductor is: 0non-zero; but uniformnon-zero; non-uniforminfinite part c: assume that at some point just outside the surface of the conductor, the electric field has magnitude e and is directed toward the surface of the conductor. what is the charge density η on the surface of the conductor at that point? express your answer in terms of e and ϵ0
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
A 12.0 μF capacitor is connected to a power supply that keeps a constant potential difference of 26....
Questions in other subjects:

English, 11.11.2020 01:00




Social Studies, 11.11.2020 01:00

Mathematics, 11.11.2020 01:00


Mathematics, 11.11.2020 01:00