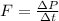Physics, 19.02.2020 02:56, mckenziew6969
During a tennis volley, a ball arrives at a player at 40 m/s is struck by the racket and returned at 40 m/s. The other player, realizing the ball is out of bounds, catches it in her hand. Compare the force exerted by the player with racket with the force exerted by the second player assuming that the time interval of contact is the same in both cases.

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Physics

Physics, 22.06.2019 01:00, winnie45
Red’s momentum vector before the collision is green’s momentum vector after the collision. question 1 options: shorter than longer than equal to question 2 (1 point) saved since green bounces off red, this must be an collision. question 2 options: explosion inelastic elastic question 3 (1 point) saved red transfers of its momentum to green during the collision. question 3 options: little all most none question 4 (4 points) why does red transfer all its momentum to green? back up your answer with information from the simulation. write at least 2 sentences. question 4 options: skip toolbars for . more insert actions. more text actions. more paragraph style actions. question 5 (1 point) now make red much heavier than green. answer the questions below to describe how both red and green behave after the collision. you might want to play the sim multiple times. click on restart or return balls to start over. to see numbers, check the show values box (inside the green box). red during the collision because it transferred some momentum to green. question 5 options: sped up kept the same velocity slowed down question 6 (1 point) green sped up during the collision as it question 6 options: lost momentum to red maintained a constant momentum. gained momentum from red question 7 (1 point) after the collision . . question 7 options: red bounced off green and went to the left. green moved to the right. both green and red stopped as they have lost all momentum. red stopped and green moved to the right. both green and red moved to the right. question 8 (4 points) only some of red’s momentum was transferred to green. why did this occur? back up your answer with information from the simulation. write at least 2 sentences. question 8 options: skip toolbars for . more insert actions. more text actions. more paragraph style actions. question 9 (1 point) now make red much lighter than green. answer the questions below to describe how both red and green behave after the collision. you might want to play the sim multiple times. click on restart or return balls to start over. to see numbers, check the show values box (inside the green box). which is true about the collision? question 9 options: green slowed down after the collision therefore it must have lost momentum. green sped up after the collision therefore it must have lost momentum. green sped up after the collision therefore it must have gained momentum. green slowed down after the collision therefore it must have gained momentum. question 10 (1 point) since green gained momentum, red had to have momentum because you cannot create or destroy momentum. question 10 options: lost kept the same amount of gained question 11 (1 point) since green was so much and harder to move, it caused red to bounce back to the left giving red . question 11 options: lighter. . . . negative heavier . . . . negative lighter. . . . positive heavier . . . . positive question 12 (4 points) now, click on more data at the bottom of the sim. play with different numbers for the masses and starting velocities. you can even make the starting velocities negative! tell me one thing you discovered by adjusting the speeds and masses. write at least 2 sentences. be specific and use words like velocity, momentum, mass, increased, decreased, etc. question 12 options: skip toolbars for . more insert actions. more text actions. more paragraph style actions. part 2: inelastic collisions question 13 (1 point) click on the "less data" box at the bottom of the sim. in the green box, slide the elasticity meter all the way to inelastic so there is 0% elasticity: make the masses whatever size suits you. make sure that green starts out with a velocity of 0 m/s – if you didn’t change this in the last step, you don’t need to do anything. push play and observe! true or false: when red and green collide, they stick together. question 13 options: true false question 14 (1 point) the velocity of red & green after the collision is the velocity that red started off with. question 14 options: larger than smaller than equal to
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 05:00, heavyhearttim
Asmall 21 kilogram canoe is floating downriver at a speed of 1 m/s. what is the canoe's kinetic energy?
Answers: 1

Physics, 22.06.2019 06:20, walmartislife
Part 1: a magnetic levitation or maglev train rides rails without touching them. explain how this works using your data. include the appropriate magnet drawing in your answer. part 2: two objects are near a bar magnet. one is about 1 cm away, while the other is 6 cm away. compare and contrast the magnetic force that affects each object. use your data to answer the question
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
During a tennis volley, a ball arrives at a player at 40 m/s is struck by the racket and returned at...
Questions in other subjects:

Mathematics, 21.01.2021 06:40



Computers and Technology, 21.01.2021 06:40

Mathematics, 21.01.2021 06:40





Mathematics, 21.01.2021 06:40