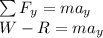Physics, 28.10.2019 21:31, keigleyhannah30
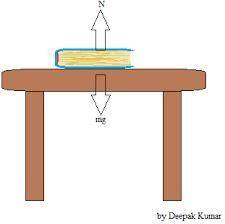
An object of mass m rests on a flat table. the earth pulls on this object with a force of magnitude mg. what is the reaction force to this pull?

Answers: 1
Similar questions

Physics, 21.09.2019 18:00, shantrice1831
Answers: 1

Physics, 09.10.2019 20:30, Jackmcvay14
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
An object of mass m rests on a flat table. the earth pulls on this object with a force of magnitude...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 03.06.2020 14:02




Mathematics, 03.06.2020 14:02

Biology, 03.06.2020 14:02

Mathematics, 03.06.2020 14:02

Health, 03.06.2020 14:02