Prove: AB ≅ AC

Mathematics, 20.10.2021 14:00, vannitling12p4w44f
Consider the diagram and proof by contradiction.
Given: △ABC with ∠B ≅ ∠C
Prove: AB ≅ AC
Triangle A B C is shown. Angles A B C and B C A are congruent.
It is given that ∠B ≅ ∠C. Assume AB and AC are not congruent. If AB > AC, then m∠C > m∠B by . If AC > AB, then m∠B > m∠C for the same reason. However, using the given statement and the definition of congruency, we know that m∠B = m∠C. Therefore, AB = AC and AB ≅ AC.
What is the missing reason in the proof?
converse of the triangle parts relationship theorem
substitution
definition of congruency
converse of the isosceles triangle theorem

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 20.06.2019 18:04, alosnomolina1122
Write a positive or negative number to represent each situation. a. you win 150 dollars in a contest b. a loss of 15 yards in a football game c. 75 feet below sea level d. 35 degrees above 0 f e. a debt of 24.75 dollars
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 13:40, jonmorton159
Although changes result from business transactions, the equality of the fundamental bookkeeping equation must remain. t/f
Answers: 2

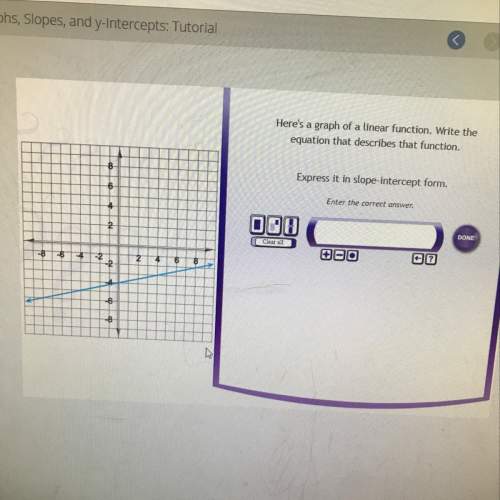
Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:30, vtrvfrfvrvfvnkjrf
What is the slope of the line shown below?
Answers: 2

Do you know the correct answer?
Consider the diagram and proof by contradiction.
Given: △ABC with ∠B ≅ ∠C
Prove: AB ≅ AC
Prove: AB ≅ AC
Questions in other subjects:



Biology, 21.08.2020 02:01

Engineering, 21.08.2020 02:01

English, 21.08.2020 02:01



Chemistry, 21.08.2020 02:01