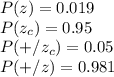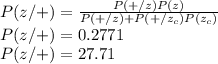Mathematics, 18.06.2021 03:20, davishernandez357
A pregnant woman lives in an area where the Zika virus is fairly rare---
1 in 1000 people have it. Still, she’s concerned, so she gets tested. There is a good but not perfect test for the virus---it gives a positive reading with probability .99 if the person has the virus and a positive reading with probability .05 if the person does not. Her reading is positive. How concerned should she be now? Probability---example We can use Bayes’ Theorem to calculate the probability she actually has the virus conditional on her positive test.
P(Z) = .001 (unconditional probability of having Zika)
P(Zc ) = .999 P(+|Z) = .99
P(+|Zc ) = .05
P(Z|+) = P(+|Z)P(Z)/{P(+|Z)P(Z) + P(+|Zc )P(Zc )} = .019
---less than 2% probability!!
The unconditional (prior) probability of her having the virus was quite low, 1/1000. We updated the probability based on the results of an imperfect test, but since it’s much more likely that the test was wrong (50 out of 1000 people without the virus test positive), our probability gets updated based on the positive test, but it doesn’t get updated that much. It goes from .0001 to .019.
Consider the example you saw in the lecture involving the Zika virus. We will start with the same set-up: A woman lives in a country where only 1 out of 1000 people has the virus. There is a test available that is positive 5% of the time when the patient does not have it, negative 1% of the time when the patient does have it, and otherwise correct. Recall that we computed that the woman’s chance of having the virus, conditional on a positive test, is less than 1.9%. (By the way, in Bayesian parlance, we call the initial, unconditional, probability the "prior" and the resulting conditional probability, after updating based on observations, the "posterior.")
6. Let the conditional probability we computed (1.9%) serve the role as the new prior. Compute the new probability that she has the virus (new posterior) based on her getting a second positive test.
7. How many positive test results would she have to receive in order to be at least 95% sure that she has the virus?
How many positive test results would she have to receive in order to be at least 95% sure that she has the virus?
Two
Three
Four
Five
Not possible to infer from the available information
In Question 6 we computed the probability of having the Zika virus after a second positive test by using the probability of having the Zika virus given a positive test (1.9%). Another way to compute this probability would be to use the fact that the two tests are independent and directly apply Bayes rule to derive the same result without using the technique employed in Question 6.
True or False: We would obtain the same probability using either method.
True
False
Not possible to infer from the available information

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:30, cameronrandom00
You’re repairing a large rectangular aquarium. the final step is to cover the glass with a protective film. the front and back of the aquarium measure 4 meters by 2 meters, and the sides of the aquarium measure 3 meters by 2 meters. how many square meters of protective film do you need? ( )
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 14:50, 2022vaneeanika51
S-7< 3 i need answering this problem someone asap answer
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:30, myohmyohmy
Nick has box brads. he uses 4 brads for the first project. nick let’s b represent the original number of brads and finds that for the second project, the number of brads he uses is 8 more than half the difference of b and 4. write an expression to represent the number of brads he uses for the second project.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:30, bxbykyah
You have learned about the six trigonometric functions, their definitions, how to use them, and how to represent them graphically. the sine, cosine, and tangent trigonometric functions can be paired with their reciprocal functions, cosecant, secant, and cotangent, respectively. think about how each function is related to its reciprocal function. how are the graphs of the reciprocal functions related to their corresponding original functions? what happens to the graphs of the reciprocal functions as x approaches the zeros of the original functions? describe how you would teach friends with different learning styles (visual-spatial, aural-auditory, verbal-linguistic, physical-bodily-kinesthetic, logical-mathematical, social-interpersonal, and solitary-intrapersonal) how to graph the reciprocal functions
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
A pregnant woman lives in an area where the Zika virus is fairly rare---
1 in 1000 people have it....
Questions in other subjects:



Biology, 23.11.2020 09:40

Mathematics, 23.11.2020 09:40

Mathematics, 23.11.2020 09:40


English, 23.11.2020 09:40



English, 23.11.2020 09:40