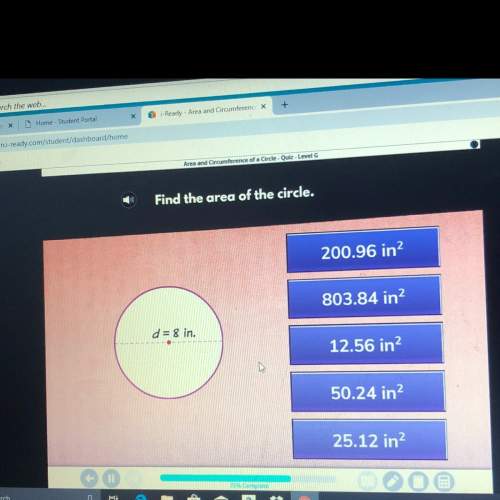
1. Create a random triangle, ΔABC. Measure and record its angles.
∠ABC =
∠ACB =
∠CAB =<...

Mathematics, 14.01.2021 01:00, mochoa4
1. Create a random triangle, ΔABC. Measure and record its angles.
∠ABC =
∠ACB =
∠CAB =
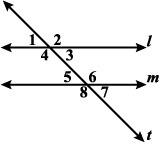
2. Now you will attempt to copy your original triangle using one of its angles
- Draw a line segment, , of any length anywhere on the coordinate plane, but not on top of ∆ABC.
- Choose one of the angles on ∆ABC. From point D, create an angle of the same size as the angle you chose. Then draw a ray from D through the angle. You should now have an angle that is congruent to the angle you chose on ∆ABC.
- Create a point anywhere outside the mouth, or opening, of the angle you created. The point will initially be named F by the tool, but you should rename it point G. Now draw a ray from E through G such that it intersects the first ray. Your creation should be a closed shape resembling a triangle.
- Label the point of intersection of the two rays F, and draw ∆DEF by creating a polygon through points D, E, and F.
-Click on point G, and move it around. By moving point G, you can change and , while keeping fixed.
Take a screenshot of your results for one position of G, save it, and insert the image in the space below.
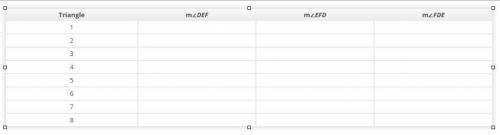
3. In GeoGebra, label the measures of the three angles on ∆DEF. Then move point G around the coordinate plane to produce triangles with different sets of angles. Record at least five sets of angles as you move G. (Screenshot is answer box)
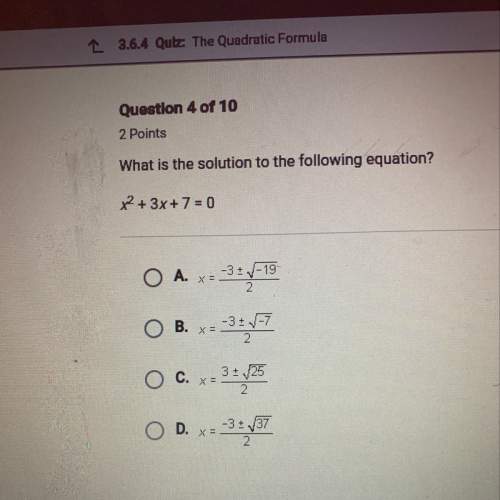
4. By moving point G, how many triangles is it possible to draw, keeping the measure of just one angle constant (in this case, m∠FDE)? In how many instances are all three angle measures of ∆DEF equal to those of the original triangle, ∆ABC?
5. To decide whether two triangles are similar, is it enough to know that one pair of corresponding angle measures is equal? Use your observations and your understanding of similarity transformations to explain your answer.

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 19:00, libertycooper
D(5, 7). e(4,3), and f(8, 2) form the vertices of a triangle. what is mzdef? oa. 30° ob. 45° oc. 60° od 90°
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:00, kennrecklezz
Which of these tools or constructions is used to inscribe a hexagon inside a circle?
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:30, psychocatgirl1
Answer asap evaluate 4-0.25g+0.5h4−0.25g+0.5h when g=10g=10 and h=5h=5.
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:20, macycj8
1. 2. ∠b and ∠y are right angles. 3.? 4.? which two statements are missing in steps 3 and 4? ∠x ≅ ∠c △abc ~ △zyx by the sas similarity theorem. ∠b ≅ ∠y △abc ~ △zyx by the sas similarity theorem. = 2 △abc ~ △zyx by the sss similarity theorem. = 2 △abc ~ △zyx by the sss similarity theorem.
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
Questions in other subjects:

French, 03.12.2020 01:00

History, 03.12.2020 01:00





Mathematics, 03.12.2020 01:00

English, 03.12.2020 01:00