
Mathematics, 22.09.2020 03:01, damienwoodlin6
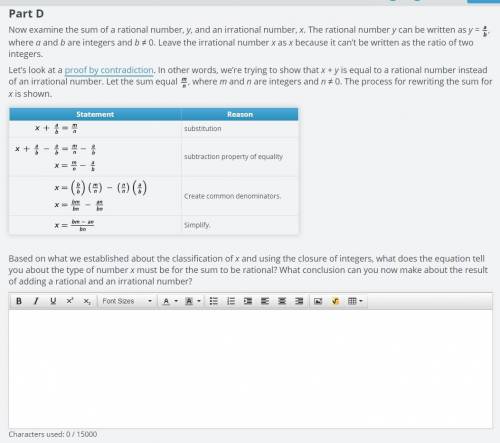
Now examine the sum of a rational number, y, and an irrational number, x. The rational number y can be written as y = , where a and b are integers and b ≠ 0. Leave the irrational number x as x because it can’t be written as the ratio of two integers. Let’s look at a proof by contradiction. In other words, we’re trying to show that x + y is equal to a rational number instead of an irrational number. Let the sum equal , where m and n are integers and n ≠ 0. The process for rewriting the sum for x is shown. Statement Reason substitution subtraction property of equality Create common denominators. Simplify. Based on what we established about the classification of x and using the closure of integers, what does the equation tell you about the type of number x must be for the sum to be rational? What conclusion can you now make about the result of adding a rational and an irrational number?

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:50, lucyamine0
The parabola y = x² - 4 opens: a.) up b.) down c.) right d.) left
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:30, Angelanova69134
Someone answer this asap rn for ! a discount store’s prices are 25% lower than department store prices. the function c(x) = 0.75x can be used to determine the cost c, in dollars, of an item, where x is the department store price, in dollars. if the item has not sold in one month, the discount store takes an additional 20% off the discounted price and an additional $5 off the total purchase. the function d(y) = 0.80y - 5 can be used to find d, the cost, in dollars, of an item that has not been sold for a month, where y is the discount store price, in dollars. create a function d(c(x)) that represents the final price of an item when a costumer buys an item that has been in the discount store for a month. d(c(x)) =
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:40, rivera8
Juliana says that she can use the patterns of equivalent ratios in the multiplication table below to write an infinite number of ratios that are equivalent to 6: 10. which statement explains whether juliana is correct? she is correct because she can multiply 6 and 10 by any number to form an equivalent ratio. she is correct because 6: 10 can be written as 1: 2 and there are an infinite number of ratios for 1: 2. she is not correct because the multiplication table does not include multiples of 10. she is not correct because 6: 10 is equivalent to 3: 5 and there are only 9 ratios in the multiplication table that are equivalent to 3: 5.
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:50, trevionc0322
Which of the following values cannot be probabilities? 0.08, 5 divided by 3, startroot 2 endroot, negative 0.59, 1, 0, 1.44, 3 divided by 5 select all the values that cannot be probabilities. a. five thirds b. 1.44 c. 1 d. startroot 2 endroot e. three fifths f. 0.08 g. 0 h. negative 0.59
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
Now examine the sum of a rational number, y, and an irrational number, x. The rational number y can...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 21.04.2020 17:42

Biology, 21.04.2020 17:42

Mathematics, 21.04.2020 17:42











