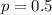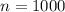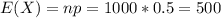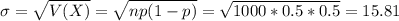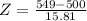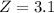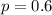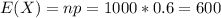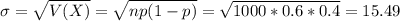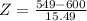Mathematics, 24.03.2020 18:37, couscous5307
Two types of coins are produced at a factory: a fair coin and a biased one that comes up heads 60 percent of the time. We have one of these coins, but do not know whether it is a fair coin or a biased one. In order to ascertain which type of coin we have, we shall perform the following statistical test: We shall toss the coin 1000 times. If the coin lands on heads 550 or more times, then we shall conclude that it is a biased coin, whereas if it lands on heads less than 550 times, then we shall conclude that it is a fair coin. Use a normal approximation to compute the following probabilities (ignore continuity correction). (i) If the coin is actually fair, what is the probability that we shall reach a false conclusion? [7] (ii) If the coin is actually unfair, what is the probability that we shall reach a false conclusion? [8] Your

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:40, stephen4438
Which of the following represents the range of the graph of f(x) below
Answers: 1

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:20, rgilliam3002
Which of the following can be used to explain a statement in a geometric proof?
Answers: 2

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 21:30, gigglegirl5802
Select all the statements that apply to this figure
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
Two types of coins are produced at a factory: a fair coin and a biased one that comes up heads 60 pe...
Questions in other subjects:



English, 08.07.2020 04:01

English, 08.07.2020 04:01






Mathematics, 08.07.2020 05:01


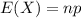
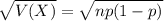
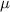 and standard deviation
and standard deviation 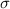 , the zscore of a measure X is given by:
, the zscore of a measure X is given by: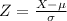
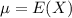 ,
, 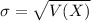 .
.