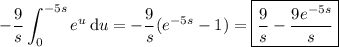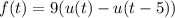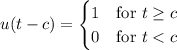Mathematics, 24.03.2020 16:51, mona92
Let f be a function defined for t ≥ 0. Then the integral ℒ{f(t)} = [infinity] e−stf(t) dt 0 is said to be the Laplace transform of f, provided that the integral converges. Find ℒ{f(t)}. (Write your answer as a function of s.) f(t) = 9, 0 ≤ t < 5 0, t ≥ 5

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00, ashl3yisbored
Determine the mean and variance of the random variable with the following probability mass function. f(x)=( 729divided by 91) (1 divided by 9) superscript x baseline comma x equals 1,2,3 round your answers to three decimal places (e. g. 98.765).
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 18:30, angelina6836
Anormally distributed data set has a mean of 176.3 and a standard deviation of 4.2. what is the approximate z-score for the data value of 167.9? 2.00 −2.00 8.4 −8.4
Answers: 2


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 20:30, janeou17xn
Peter applied to an accounting firm and a consulting firm. he knows that 30% of similarly qualified applicants receive job offers from the accounting firm, while only 20% of similarly qualified applicants receive job offers from the consulting firm. assume that receiving an offer from one firm is independent of receiving an offer from the other. what is the probability that both firms offer peter a job?
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
Let f be a function defined for t ≥ 0. Then the integral ℒ{f(t)} = [infinity] e−stf(t) dt 0 is said...
Questions in other subjects:

Biology, 28.07.2019 07:00

Biology, 28.07.2019 07:00

Chemistry, 28.07.2019 07:00


History, 28.07.2019 07:00


History, 28.07.2019 07:00




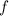 , we have
, we have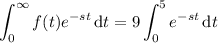
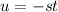 , so that
, so that 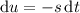 .
.