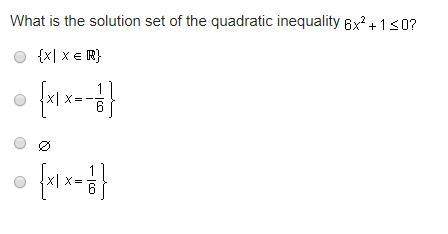Mathematics, 07.03.2020 04:15, brysong
For an n×n matrix, A, the trace of A is defined as the sum of the entries on the main diagonal. That is, tr(A)=a11+a22+?+ann.
(a) Prove that for any matrices A and B having the same size, tr(A+B)=tr(A)+tr(B) and for any scalar c, tr(cA)=ctr(A)
(b) Prove tr(A)=tr(AT) for all square matrices A.
(c) Prove that for any matrices A and B having the same size, tr(AB)=tr(BA).
(d) Using (c), prove that if A and B are similar tr(A)=tr(B).

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Mathematics

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 16:00, ashley1460
Let the closed interval [a , b] be the domain of function f. the domain of f(x - 3) is given by (a) the open interval (a , b) (b) the closed interval [a , b] (c) the closed interval [a - 3 , b - 3] (d) the closed interval [a + 3 , b + 3]
Answers: 2


Mathematics, 21.06.2019 22:30, Edwardwall
What three-dimensional solid have 6 rectangular faces, 2 equal bases that are not rectangles and 18 edges
Answers: 3

Mathematics, 21.06.2019 23:40, asiababbie33
Agrid shows the positions of a subway stop and your house. the subway stop is located at (-5,2) and your house is located at (-9,9). what is the distance, to the nearest unit, between your house and the subway stop?
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
For an n×n matrix, A, the trace of A is defined as the sum of the entries on the main diagonal. That...
Questions in other subjects:









Mathematics, 24.05.2021 16:00