
Engineering, 08.09.2021 19:10, QUEEN2267
Assignment Summary
For this assignment, you will apply what you know about the technological design process to solve an Earth Science–related problem in your community.
Background Information
Engineers and scientists are problem solvers. They design and make products that help solve problems such as pollution, erosion, and even climate change. The products they make help keep Earth healthy. For example, engineers have designed the equipment in water treatment plants to improve the quality of water used by homes and businesses. This equipment allows water to be reused and reintroduced into the water cycle without harming the environment or living things on Earth. The technological design process is useful in addressing large- and small-scale problems.
Materials
Varies by prototype/model Assignment Instructions
For this project, you are expected to submit the following:
1. Your Student Guide with completed Student Worksheet
2. Your prototype or model
Step 1: Prepare for the project.
a) Read through the guide before you begin so you know the expectations for this project.
b) If anything is not clear to you, be sure to ask your teacher.
Step 2: Identify a problem or need in your community that can be solved by applying the
technological design process.
a) Choose a problem that is Earth Science–related, such as decreasing pollution, erosion, or damage due to natural disasters. Describe the problem in the appropriate space in the Student Worksheet.
b) Research related information that will tell you more about the problem or help you solve it.
i. Be sure to use reliable sources.
ii. Record your findings in the appropriate space in the Student Worksheet.
iii. List the sources you used at the end of the Student Worksheet.
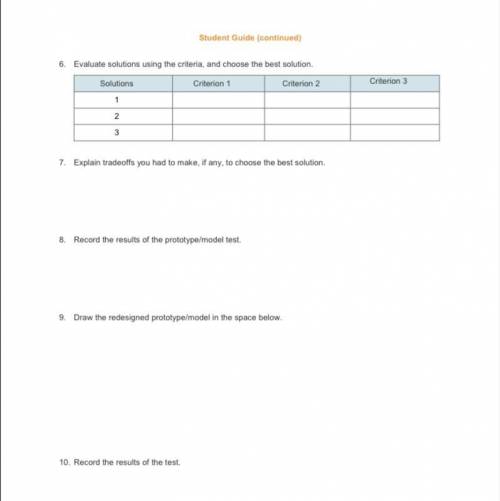
Step 3: Design solutions to the problem.
a) Establish criteria that your solution should meet. List them from most important to least important
in the appropriate space in the Student Worksheet.
b) Draw prototypes/models of possible solutions in the appropriate space in the
c) Evaluate the possible solutions against the criteria. Use the table in the Student Worksheet to evaluate the possible solutions. Add more columns and rows if necessary.
d) Choose the best solution. Highlight the best solution in the table in the Student Worksheet and explain the tradeoffs you had to make, if any.
Step 4: Implement the solution.
a) Prepare the materials you need to build a prototype/model.
b) Build a prototype/model of the product.
c) Test the prototype/model.
d) Analyze the results of your test. Record your findings in the appropriate space in the Student Worksheet.
e) If your test shows that your product/model is successful, submit your prototype/model to your teacher. Be sure to put your name on it. Then, proceed to step 6. If your test is not successful, continue to step 5.
Step 5: Redesign and retest solution (if necessary).
a) Adjust the design of your prototype as necessary. Draw your redesigned prototype/model in the
space provided in the Student Worksheet.
b) Retest the prototype/model.
c) Analyze the results of your test. Record your findings in the appropriate space in the Student Worksheet.
d) Submit your prototype/model to your teacher. Be sure to put your name on it.
Step 6: Evaluate your project using this checklist.
If you can check each box below, you are ready to submit your project.
Did you identify an Earth Science–related problem in your community?
Did you do related research to help you solve the problem?
Did you list your sources at the end of the Student Worksheet?
Did you establish criteria for your solution? Did you list the criteria in order from most important to
least important?
Did you draw prototypes/models of possible solutions?
Did you evaluate possible solutions against the criteria?
Did you choose the best solution? Did you highlight the best solution in the table?
Did you explain tradeoffs you had to make, if any?
Did you create a prototype/model of the best solution?
Did you test your prototype/model? Did you record the results of your test?
Did you redesign your prototype/model if the original prototype/model did not work the way it was
supposed to?
Did you test your new prototype/model? Did you record the results of your test?
Did you complete your Student Worksheet and submit it online?
Student Guide (continued)
Did you submit your prototype/model to your teacher? Step 7: Revise and submit your project.
a) If you were unable to check off all the requirements on the checklist, go back and make sure that your project is complete. Save your project before submitting it.
b) Turn in your prototype/model to your teacher.
c) Submit your Student Guide through the Virtual Classroom.
d) Congratulations! You have completed your project.
Student Guide (continued)

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Engineering

Engineering, 03.07.2019 14:10, volleyballfun24
If the thermal strain developed in polyimide film during deposition is given as 0.0044. assume room temperature is kept at 17.3 c, and thermal coefficient of expansion for the film and the substrate are 54 x 10^-6c^-1 and 3.3 x 10^-6c^-1respectively. calculate the deposition temperature.
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20, luisgonz5050
Find the kinematic pressure of 160kpa. for air, r-287 j/ kg k. and hair al viscosity of air at a temperature of 50°c and an absolute (10 points) (b) find the dynamic viscosity of air at 110 °c. sutherland constant for air is 111k
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20, rjone8429
Asimple rankine cycle uses water as the working fluid. the water enters the turbine at 10 mpa and 480c while the condenser operates at 6 kpa. if the turbine has an isentropic efficiency of 80 percent while the pump has an isentropic efficiency of 70 percent determine the thermal efficiency
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:10, nbunny7208
What is the chief metrological difference between measuring with a microscope and with an electronic comparator? a. the microscope is limited to small workpieces. a. the microscope is limited to small workpieces. c. the comparator can only examine one point on the workpiece. d. the microscope carries its own standard.
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
Assignment Summary
For this assignment, you will apply what you know about the technological desig...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 19.03.2021 14:00




History, 19.03.2021 14:00









