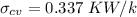Engineering, 23.05.2020 02:01, kayonapretty14p45995
Air at 200 kPa, 528C, and a velocity of 355 m/s enters an insulated duct of varying cross-sectional area. The air exits at 100 kPa, 82°C. At the inlet, the cross-sectional area is 6.57 2 c m 2 .

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Engineering

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10, winterblanco
The higher the astm grain-size number, the coarser the grain is. a)-true b)-false
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10, wirchakethan23
Hydraulic fluid with a sg. of 0.78 is flowing through a 1.5 in. i. d. pipe at 58 gal/min. the fluid has an absolute viscosity of 11.8 x 105 lbf-sec/ft2. is the flow laminar, turbulent or within the critical range? give both a numerical reynolds number and a term answer.
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10, katelynn73
Atmospheric air has a temperature (dry bulb) of 80° f and a wet bulb temperature of 60° f when the barometric pressure is 14.696 psia. determine the specific humidity, grains/lb dry air. a. 11.4 c. 55.8 d. 22.5 b. 44.1
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10, jojoangelique13
The flow rate of air through a through a pipe is 0.02 m5/s. a pitot static tube is placed in the flow. the radius of the pitot static tube is 1 mm. assuming the flow to be steady and the air to be at 300k, calculate the difference in total and static pressure if the diameter of the pipe is: (a) d 0.1 m d 0.05 m (c) d 0.01 m
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
Air at 200 kPa, 528C, and a velocity of 355 m/s enters an insulated duct of varying cross-sectional...
Questions in other subjects:


History, 26.05.2021 21:20

Mathematics, 26.05.2021 21:20


Mathematics, 26.05.2021 21:20

Biology, 26.05.2021 21:20


Social Studies, 26.05.2021 21:20



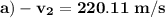

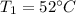
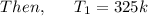
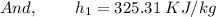
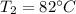
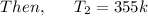
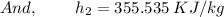
![m\left [\left (h_1-h_2 \right )+\frac{v_1^2-v_2^2}{2} \right ]=0](/tpl/images/0662/8536/aca89.png)

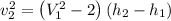
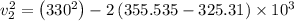

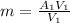


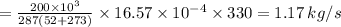
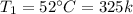
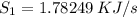

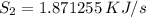
![\sigma_{cv}=m[S_2-S_1-R\;ln(\frac{P_2}{P_1}) ]](/tpl/images/0662/8536/d70a6.png)
![=1.17\left[1.871255-1.78249-0.287\;ln\left(\frac{100}{200} \right)\right]](/tpl/images/0662/8536/60410.png)