Engineering, 22.02.2020 00:46, slbucknerholmes9
A mass of 1.9 kg of air at 120 kPa and 24°C is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston–cylinder device. The air is now compressed to a final pressure of 600 kPa. During the process, heat is transferred from the air such that the temperature inside the cylinder remains constant. Calculate the work input during this process. Take the gas constant of air as R = 0.287 kJ/kg·K.

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Engineering

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:10, katelynn73
Atmospheric air has a temperature (dry bulb) of 80° f and a wet bulb temperature of 60° f when the barometric pressure is 14.696 psia. determine the specific humidity, grains/lb dry air. a. 11.4 c. 55.8 d. 22.5 b. 44.1
Answers: 1

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20, kendrawalraven
The characteristic roots of a dynamic system are: 1.7920 1.8160 i, -1.7920 1.8160 i, -0.4160 what is the order of this system? what are the settling time and damping ratio of the system?
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 18:20, cxttiemsp021
Atank with constant volume contains 2.27 kg of a mixture of water phases (liquid-vapor). in the initial state the temperature and the quality are 127 °c and 0.6, respectively. the mixture is heated until the temperature of 160 oc is reached. illustrate the process in a t-v diagram. then, determine (1) the mass of the vapor in kg at the initial state, (2) the final pressure in kpa.
Answers: 3

Engineering, 04.07.2019 19:10, gabigalvis1091
What is the main objective of using reheat rankine cycle?
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
A mass of 1.9 kg of air at 120 kPa and 24°C is contained in a gas-tight, frictionless piston–cylinde...
Questions in other subjects:


Biology, 10.08.2019 03:10




Biology, 10.08.2019 03:10





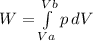
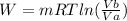 . As we have pressure as a known values, we can re-write the equation, using pressures:
. As we have pressure as a known values, we can re-write the equation, using pressures: