
Chemistry, 20.12.2021 22:10, jesuscruzm2020
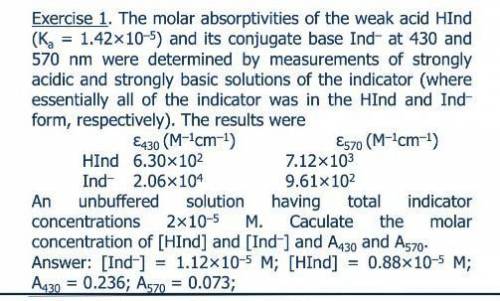
The molar absorptivities at 430 and 570 nm of the weak acid HIn (Ka = 1.42 ? 10-5) and its conjugate base In- were determined by measurements of strongly acidic and strongly basic solutions of the indicator. Under this conditions, essentially all of the indicator was in the HIn and In- form, respectively. The molar ab-sorptivities of HIn and In- at 430 nm and 570 nm were 6.30 ? 102 and 7.12 ? 103, and 2.06 ? 104 and 9.61 ? 102, respectively. Calculate absorbance data for unbuffered solutions that have total indicator concentrations ranging from 2 ? 10-5 to 16 ? 10-5 M.

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 06:30, reecedstceklein
Over the last 90 years, scientists have added to the body of evidence supporting the big bang theory. what is the latest piece of evidence discovered in 2014?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 02:00, raulflores01
Which best describes the present-day universe? opaque, expanding very slowly, stars produce heavy elements transparent, expanding at an accelerated rate, stars produce heavy elements opaque, expanding at an accelerated rate, stars produce only hydrogen and helium transparent, expanding very slowly, stars produce only hydrogen and helium
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 03:30, rniadsharri16
Select the correct lewis structure for fluorine which is group 7a element?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 15:30, tristen2001
Select the correct answer. the gas in a sealed container has an absolute pressure of 125.4 kilopascals. if the air around the container is at a pressure of 99.8 kilopascals, what is thegauge pressure inside the container?
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
The molar absorptivities at 430 and 570 nm of the weak acid HIn (Ka = 1.42 ? 10-5) and its conjugate...
Questions in other subjects:




Social Studies, 11.12.2019 22:31











