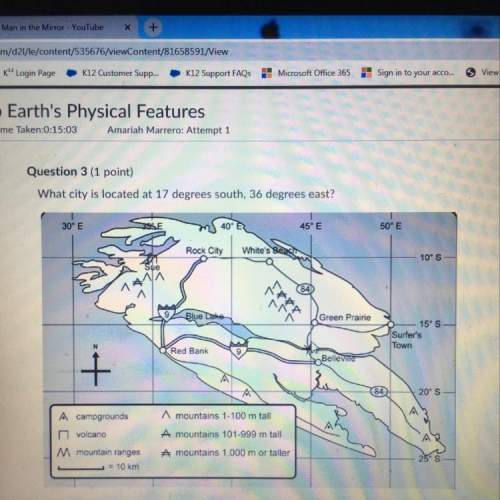
Consider the following intermediate chemical equations.
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H, 0(1)
H2(g)+F2(g)...

Chemistry, 30.06.2020 04:01, ineedhelp2285
Consider the following intermediate chemical equations.
2H2(g) + O2(g) → 2H, 0(1)
H2(g)+F2(g) → 2HF(9)
In the final chemical equation, HF and O2 are the products that are formed through the reaction between H2O and F2. Before
you can add these intermediate chemical equations, you need to alter them by multiplying the
o second equation by 2 and reversing the first equation.
first equation by 2 and reversing it.
first equation by (1/2) and reversing the second equation
O second equation by 2 and reversing it.

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Chemistry

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 16:50, ddmoorehouseov75lc
If a substance is not at its melting or boiling point, as the heat content of a sample of matter increases, its temperature increases the number of intermolecular bonds decreases the space between particles increases the particles move faster
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 21.06.2019 17:00, kathleendthomas
Look at the reaction below: ca(hco3)2 --> caco3 + co2 + h2o first, balance the reaction. once balanced, use dimensional analysis or another method to find out how many moles of carbon dioxide will be produced if we start with 16.5 moles of calcium bicarbonate (calcium hydrogen carbonate). = mol of co2 number needs to be reported to three significant figures.
Answers: 1

Do you know the correct answer?
Questions in other subjects:

Biology, 18.07.2019 03:00





History, 18.07.2019 03:00


History, 18.07.2019 03:00

Mathematics, 18.07.2019 03:00