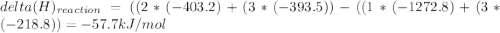Chemistry, 05.05.2020 08:30, jackiediaz
Use the given heats of formation to calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction. B2O3(g) + 3COCl2(g) →2BCl3(g) + 3CO2(g) ΔHof of B2O3(g) is –1272.8 kJ∙mol–1 ΔHof of BCl3(g) is –403.8 kJ∙mol–1 ΔHof of COCl2(g) is –218.8 kJ∙mol–1 ΔHof of CO2(g) is –393.5 kJ∙mol–1 Question 8 options: 1) 649.3 kJ·mol–1 2) 354.9 kJ·mol–1 3) –58.9 kJ·mol–1 4) –3917.3 kJ·mol–1

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 00:00, brookemcelhaney
Which of the following methods uses the decay of atomic particles in an object to find its exact age? a. fossil dating b. geologic dating c. radioactive dating d. relative dating
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 02:30, drivinghydra
What is the relation between concentration of reactants and the rate of chemical reaction?
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 12:10, purplefish53
Consider the reaction: n2(g) + o2(g) ⇄ 2no(g) kc = 0.10 at 2000oc starting with initial concentrations of 0.040 mol/l of n2 and 0.040 mol/l of o2, calculate the equilibrium concentration of no in mol/l how would this be done?
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
Use the given heats of formation to calculate the enthalpy change for this reaction. B2O3(g) + 3COCl...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 05.10.2019 08:30

Mathematics, 05.10.2019 08:30


History, 05.10.2019 08:30

Mathematics, 05.10.2019 08:30


Mathematics, 05.10.2019 08:30

Biology, 05.10.2019 08:30

Biology, 05.10.2019 08:30