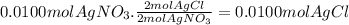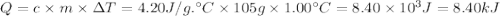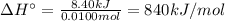Chemistry, 15.10.2019 20:30, coryintheswamp
10. when 50.0 ml of 0.200 m agno3 and 50.0 ml of 0.100 m cacl2, both at 25.0°c, are reacted in a coffee-cup calorimeter, the temperature of the reacting mixture increases to 26.0°c. calculate ∆h in kj per mole of agcl produced. assume the density of the solution is 1.05 g/ml and the specific heat capacity of the solution 4.20 j/g°c. agno3(aq) + hcl(aq) à agcl(s) + hno3(aq)

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Chemistry

Chemistry, 22.06.2019 08:30, jalst6084
7. using your knowledge of colligative properties explain whether sodium chloride or calcium chloride would be a more effective substance to melt the ice on a slick sidewalk. use 3 – 4 sentences in your explanation. 8. when a 2.5 mol of sugar (c12h22o11) are added to a certain amount of water the boiling point is raised by 1 celsius degree. if 2.5 mol of aluminum nitrate is added to the same amount of water, by how much will the boiling point be changed? show all calculations leading to your answer or use 3 – 4 sentences to explain your answer. 9. if 5.40 kcal of heat is added to 1.00 kg of water at 100⁰c, how much steam at 100⁰c is produced? show all calculations leading to an answer. 10. the freezing of water at 0⁰c can be represented as follows: h2o (l) ↔ h2o(s) the density of liquid water is 1.00 g/cm3. the density of ice is 0.92 g/cm3. in 3 – 4 sentences explain why applying pressure causes ice to melt.
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 04:20, lelliott86
The lewis diagrams for magnesium and fluorine are shown below. what is the correct chemical formula for magnesium fluoride? a. mgf b. mg2f c. mgf2 d. mg2f3
Answers: 1

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 07:30, bryantjorell
Which statement is actually true about the relationship between activation energy and reaction rates? low activation energy barriers result in low rates. high activation energy barriers result in low rates. low activation energy barriers result in no reaction. high activation energy barriers result in no reaction.
Answers: 2

Chemistry, 23.06.2019 09:20, jahnasiahill5349
Description: biological systems 5 differ from chemical systems when it comes to equilibrium. in a chemical system once equilibrium is met, no other reactions occur. in a biological system, a dynamic equilibrium is used when a substrate is turned into a product, another reaction creates the same substrate thus keeping the concentrations stagnant. this allows for cells to continually make new compounds without messing the delta g for the systems instructions: write a response to the following prompt and then respond to your peers. your individual response is due thursday at midnight (cst) your response to your peers is due saturday at midnight (cst) prompt: propose what would happen if a living cell all the sudden reached chemical equilibrium. also discuss the effects of build up of a particular substrate on a biological system. how would this affect overall delta g's?
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
10. when 50.0 ml of 0.200 m agno3 and 50.0 ml of 0.100 m cacl2, both at 25.0°c, are reacted in a cof...
Questions in other subjects:

Social Studies, 28.01.2021 05:20


Mathematics, 28.01.2021 05:20



Chemistry, 28.01.2021 05:20

Mathematics, 28.01.2021 05:20

Mathematics, 28.01.2021 05:20


Mathematics, 28.01.2021 05:20