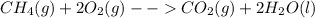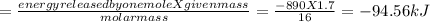Chemistry, 03.08.2019 00:20, jtorres0520
In the presence of excess oxygen, methane gas burns in a constant-pressure system to yield carbon dioxide and water: ch4 (g) 2o2 (g) → co2 (g) 2h2o(l) δh = -890.0 kj
calculate the value of q (kj) in this exothermic reaction when 1.70 g of methane is combusted at constant pressure.
(a) -94.6 kj
(b) 0.0306 kj
(c) -0.0106 kj
(d) 32.7 kj
(e) -9.46 × 10^4 kj

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Chemistry


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 02:00, natalie857123
For each of the following types of reactions, write a general reaction formula in the symbolic form—for example, a + b → ab. single-displacement double-displacement synthesis decomposition
Answers: 1


Chemistry, 22.06.2019 08:00, wizz4865
Why is the bond angle in a water molecule less than the bond angle of methane? a. the central oxygen atom in water has two lone pairs of electrons, whereas the central carbon atom in methane has no lone pairs. b. the central hydrogen atom in water has one lone pair of electrons, whereas the central carbon atom in methane has two lone pairs. c. the central oxygen atom in water has four lone pairs of electrons, whereas the central carbon atom in methane has only one lone pair. d. the central oxygen atom exerts more repulsive force on surrounding atoms than the central carbon atom in methane does. reset next
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
In the presence of excess oxygen, methane gas burns in a constant-pressure system to yield carbon di...
Questions in other subjects:

History, 25.07.2019 02:00


Biology, 25.07.2019 02:00

History, 25.07.2019 02:00

Biology, 25.07.2019 02:00




Mathematics, 25.07.2019 02:00