
Biology, 16.05.2021 14:00, mgavyn9457
Usable chemical energy on Earth begins as light energy, usually solar energy. Plants and other autotrophs convert solar energy to
Chemical energy via the process of photosynthesis. Carbon dioxide and water, in the presence of light, are transformed into glucose.
The chemical energy is stored in the chemical bonds of glucose and is released during the process of cellular respiration. Cellular
respiration releases the chemical energy stored in food molecules to produce high-energy ATP molecules. Macromolecules such as
carbohydrates and fats can be used as fuels for the production of ATP. All foods contain chemical energy, but the amount of chemical
energy is dependent of the type of food. The larger the compound, the more chemical bonds present and the greater amount of
available chemical energy. We can rank molecule size, from smallest to largest, as sugar, starch, fat. We refer to the stored chemical
energy in foods as calories. A calorie is the amount of energy required to raise the temperature of 1 gram of water 1 degree Celsius.
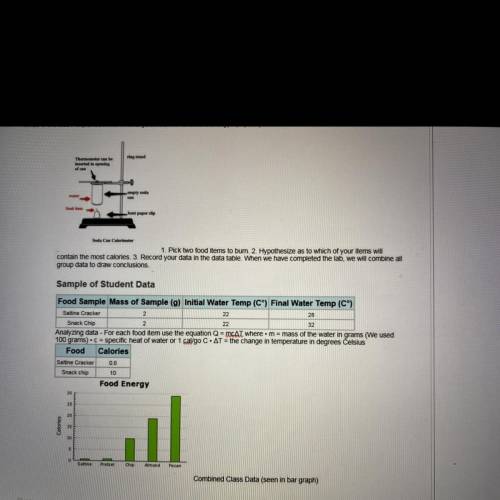
When we refer to the calories in food, we are really talking about kilocalories or 1000 calories. Biology students "burned" 2 grams of
food to heat water in a calorimeter in order to determine which food items contain the most usable chemical energy.
Almonds may be small, but they pack a great number of nutrients, including protein, vitamin E, and vitamin B2. Almonds also contain
antioxidants and monounsaturated fat, a "good" type of fat that, like the omega-3 fatty acids, reduces the risk of heart disease.
Review the graph that represents the whole class data. Notice that the almond samples provide a large amount of chemical energy.
What is the BEST explanation for this large amount of available energy? (1 point)

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:30, chozz2783
Match the descriptions / definitions with the term they best describe 1. three dimensional relationship of the different polypeptide chains in a multisubunit protein or protein complex 2. common folding pattern in proteins in which a linear sequence of amino acids folds into a right-handed coil stabilized by internal hydrogen-bonding between polypeptide backbone atoms. 3. the amino acid sequence of a protein 4. a region on the surface of a protein that can interact with another molecule through noncovalent bonding. 5. three-dimensional arrangement of alpha-helices and beta-sheets within a single polypeptide, typically stabilized by a variety of noncovalent bonds, including ionic and hydrogen bonds, and nonpolar interactions / hydrophobic force. 6. the chain of repeating carbon and nitrogen atoms, linked by peptide bonds, in a protein. 7. common structural motif in proteins in which different sections of the polypeptide chain run alongside each other and are joined together by hydrogen bonding between atoms of the polypeptide backbone. 8. portion of a polypeptide chain that has a discrete tertiary structure of its own and can often fold independently of the rest of the chain 9. regular local folding patterns in a protein, including alpha-helix and beta-sheet a. primary structure b. beta-sheet c. protein d. coiled-coil e. polypeptide backbone f. secondary structure g. side chain h. tertiary structure i. binding site j. alpha-helix k. quaternary structure l. protein domain
Answers: 2

Biology, 21.06.2019 21:00, Kingmoney959
Leila has dimples because she received a gene copy from her father that coded for dimples. this means that dimples are an example of a trait that is
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 05:00, shreyapatel2004
Match each term to its best definition? sedimentary depositional enviornment
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
Usable chemical energy on Earth begins as light energy, usually solar energy. Plants and other autot...
Questions in other subjects:



Mathematics, 02.09.2020 18:01


Social Studies, 02.09.2020 18:01

Health, 02.09.2020 18:01

English, 02.09.2020 18:01








