
Biology, 19.04.2021 04:10, gabbypittman20
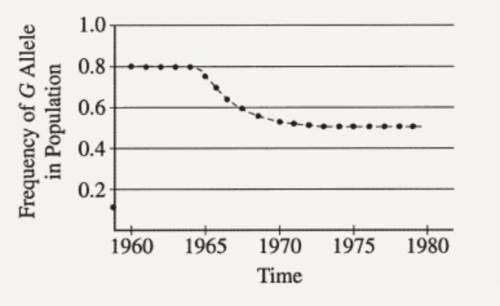
A moth's color is controlled by two alleles, G and g, at a single locus. G (gray) is dominant to g (white). A large population of moths was studied, and the frequency of the G allele in the population over time was documented, as shown in the figure below. In 1980 a random sample of 2,000 pupae was collected and moths were allowed to emerge. Assuming that the population was in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium for the G locus, what percentage of the gray moths that emerged in 1980 was heterozygous? (The Answer is 67%, can you please explain why it's 67%? thank you!!)

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 20:20, jaylahlove77
2. what process do mrna and trna work together to complete? (3 points)
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 19:00, jeanlucceltrick09
What is the next step in muscle contraction after the actin changes shape
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 20:30, kakalli9999
How is synaptic signaling different from paracrine signaling?
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 21:00, jandrew2052
One student group hypothesized that the dry baker's yeast must be alive. the temperature change, odor, and bubble foation, they said, indicated whych characteristic of life
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
A moth's color is controlled by two alleles, G and g, at a single locus. G (gray) is dominant to g (...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 28.04.2021 19:10

Mathematics, 28.04.2021 19:10


Mathematics, 28.04.2021 19:10

Mathematics, 28.04.2021 19:10









