
Biology, 16.04.2021 05:00, nathalyviruete
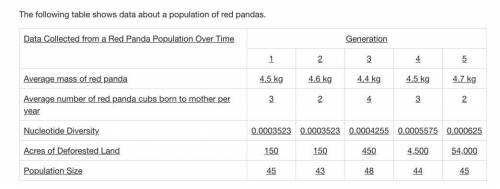
2. Which explanation for the increase in genetic diversity of this red panda population is supported by this data?
(1 point)
Red pandas in this population have encountered new predators due to the increase in deforested land, and this new predation pressure has selected for different adaptations.
Red pandas in this population have increased the number of cubs birthed by each mother every year, and this increase in population has resulted in more genetic diversity.
Red pandas in this population have encountered new environmental challenges presented by the increase in deforested land, and this has selected for different adaptations over time.
Red pandas in this population have started eating a new diet due to the increase in deforested land, and the new dietary conditions have selected for different adaptations.
5. Which of the following scenarios would reduce the number of inheritable traits in a population, causing the individuals in that population to remain very similar to one another?(1 point)
A swamp that is being drained in order to build houses.
A forest that is being converted into farmland.
A lake that is drying up due to shifts in river flow.
A desert that has existed for millennia.

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 22.06.2019 00:30, stgitskaysie9028
Each pair of clay balls represents two planetesimals. if each planetesimal is composed of the same material and is separated he the same distance, which pair experiences the frayed gravitational attraction?
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 04:00, zegangke1651
Will mark brainliest i only need the ! 1.use ten beads and a centromere of one color to construct the long chromosome. use ten beads and a centromere of a second color to construct the second chromosome in the long pair. make a drawing of the chromosomes in the space below. 2. for the second pair of chromosomes, use only five beads. 3. now model the replication of the chromosomes. make a drawing of your model in the space below. part b: meiosis i during meiosis i, the cell divides into two diploid daughter cells. 4. pair up the chromosomes to form tetrads. use the longer tetrad to model crossing-over. make a drawing of the tetrads in the space below. 5. line up the tetrads across the center of your “cell.” then model what happens to the chromosomes during anaphase i. 6. divide the cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the result. part c: meiosis ii during meiosis ii, the daughter cells divide again. 7. line up the chromosomes at the center of the first cell, one above the other. separate the chromatids in each chromosome and move them to opposite sides of the cell. 8. repeat step 7 for the second cell. 9. divide each cell into two daughter cells. use the space below to make a drawing of the four haploid cells
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 04:00, tejasheree
Asap indicate the coat color and the proportion of offspring with that color for each of the following crosses of rabbits. assume all are homozygous. alleles: a=agouti, c=chinchilla, a=albino, a is dominant over c and a, c is dominant over a agouti x chinchilla a) 1/2 chinchilla, 1/2 agouti b) 3/4 chinchilla, 1/4 agouti c) all agouti
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
2. Which explanation for the increase in genetic diversity of this red panda population is supported...
Questions in other subjects:


Mathematics, 27.07.2019 00:30

Mathematics, 27.07.2019 00:30













