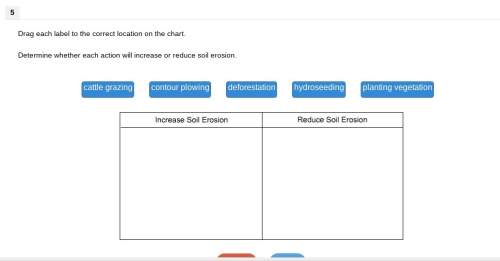
Biology, 31.05.2020 02:58, JohnnyR7057
A farmer has two homozygous varieties of tomatoes. One variety, called Little Pete, has fruits that average only 2 cm in diameter. The other variety, Big Boy, has fruits that average a whopping 14 cm in diameter. The farmer crosses Little Pete and Big Boy; he then intercrosses the F1 to produce F2 progeny. He grows 2000 F2 tomato plants and doesn’t find any F2 offspring that produce fruits as small as Little Pete or as large as Big Boy. If we assume that the differences in fruit size of these varieties are produced by genes with equal and additive effects, what can we conclude about the minimum number of loci with pairs of alleles determining the differences in fruit size of the two varieties?

Answers: 2
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 13:30, jonmorton159
Why aren't the stains like crystal violet and safranin washed away with water during simple staining?
Answers: 2

Biology, 21.06.2019 21:30, yasyyas646646
Which best explains why there are 64 possible codons in the genetic code and only 20 amino acids that make protiens of living organisms on earth
Answers: 3


Biology, 22.06.2019 05:30, maddireigh6403
How is transcription similar to translation in terms of base pairing?
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
A farmer has two homozygous varieties of tomatoes. One variety, called Little Pete, has fruits that...
Questions in other subjects: