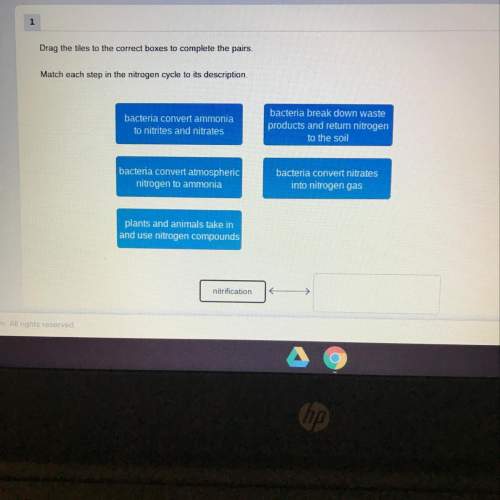
Biology, 31.03.2020 04:43, taylordalton93
Complete glucose breakdown requires the presence of oxygen to keep the working so that ATP is produced. When oxygen is absent, an anaerobic process called fermentation occurs instead, producing fewer ATP molecules overall. During this process, glycolysis proceeds as normal with glucose splitting into 2 molecules, which are then phosphorylated into 2 molecules, and finally converted into 2 molecules. However, at this point, the 2 molecules are , freeing NAD⁺ to return to the glycolytic pathway. The results of are ATP molecules and 2 molecules in animals and bacteria or 2 molecules in plants and yeast. Because these molecules enter the citric acid cycle or the electron transport chain, the net gain for fermentation is ATP molecules, compared to ATP molecules in cellular respiration.

Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 19:30, lilrariwmb23701
Which type of organism is missing from the food web seen in the illustration? primary consumers decomposers primary producers secondary consumers
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 06:20, rosie20052019
What makes a dominant allele different from a recessive allele
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 07:30, sawyerharper
Which locations on the map are low-pressure areas? a b c d e
Answers: 1
Do you know the correct answer?
Complete glucose breakdown requires the presence of oxygen to keep the working so that ATP is produ...
Questions in other subjects:




Mathematics, 22.06.2020 08:57

Mathematics, 22.06.2020 08:57

Mathematics, 22.06.2020 08:57

Mathematics, 22.06.2020 08:57


Mathematics, 22.06.2020 08:57