First person to answer correctly gets brainliest!
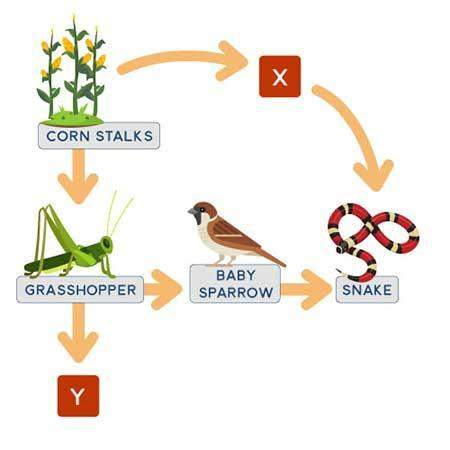
the diagram below shows a food web in...

First person to answer correctly gets brainliest!
the diagram below shows a food web in a woodland.
a food web diagram showing cornstalks with two arrows pointing away from it. one of the arrows points to the letter x and the other arrow points to a grasshopper. there are two arrows pointing away from the grasshopper. one is pointing to a baby sparrow and the other to the letter y. there is an arrow pointing away from the baby sparrow to a snake and an arrow pointing away from the letter x to the snake.
if a certain organism is a primary consumer, what best explains its position in the food web?
x, because organism x has the same role as the grasshopper
y, because organism y has the same role as grasshopper
x, because organism x has the same role as the baby sparrow
y, because organism y has the same role as the baby sparrow

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 19:10, daeshawnc14
What have we learned from fossil evidence about evolution? a) it is an abrupt change. b)the process is observable. c) it takes place during one lifetime only. d)the most complex traits are always selected.
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 01:30, eguilford4438
Scenario 5 1) take 10 red and 10 black beans and place them, mixed, on the table. record the starting phenotype # and frequencies (% of your total population) of your starting population in the table provided (generation 0). 2) act as a predator. “capture” as many organisms as you can until you have reduced the population to three organisms. put them aside. at this point, the predators die. 3) the remaining organisms each produce 2 clonal offspring. multiply your organisms accordingly and allow them to mix on the table. calculate and record the resultant phenotype # and frequencies (% of your total population) of your population in the table provided (generation 1). 4) repeat the reproduction event, allowing each of your organisms to produce 2 clonal offspring. calculate and record the resultant phenotype # and frequencies (% of your total population) of your population in the table provided (generation 2). 5) repeat the reproduction event, allowing each of your organisms to produce 2 clonal offspring. calculate and record the resultant phenotype # and frequencies (% of your total population) of your population in the table provided (generation 3).
Answers: 1

Biology, 22.06.2019 02:10, eriks1818
Scenario #2 in 2001, a population of 2,500 poison dart frogs lived in the amazon rain forest. due to increased deforestation, the population dwindled to 25 frogs in 2019. new government regulations were enacted in 2022, successfully putting an end to the deforestation of the amazon rain forest. once deforestation was stopped, the poison dart frog population was able to recover. by 2050, the population reached 8,000 frogs, of that population, 20 are homozygous recessive for being spotted (ss genotype). q2- ? q- p- p2- 2pq-
Answers: 2

Biology, 22.06.2019 07:20, Maria3737
What are the two causes of density in deep current waters? a. salinity (how much salt) of the water and high temperaturesb. salinity (how much salt) of the water and low temperatures c. oxygen content of the water and high temperatures. d. oxygen content of the water and low temperatures
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
Questions in other subjects:

Physics, 08.12.2020 08:20


Mathematics, 08.12.2020 08:20



Mathematics, 08.12.2020 08:20

Mathematics, 08.12.2020 08:20

Mathematics, 08.12.2020 08:20

History, 08.12.2020 08:20






