Biology, 08.10.2019 19:30, Angeldelissa
11. a red and a white snapdragon are crossed, and their offspring is pink. this is an example of
a. mendel's law of independent assortment.
b. mendel's law of dominance.
c. incomplete dominance.
d. codominance
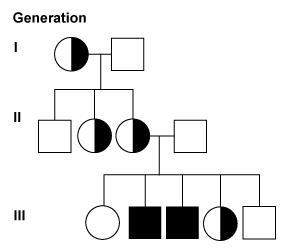
12. ( figure is the first picture: refer to the figure showing a pedigree of a family affected by a sex-linked recessive disorder. if a female is a carrier for a sex-linked recessive disorder, is it possible for her sons to be unaffected by the disorder? choose the best answer and explanation.
a. yes, this is possible. males receive an x chromosome from their mother. if their mother is a carrier, a male has a 50 percent chance of being affected by the disease and a 50 percent chance of being unaffected.
b. no, this isn't possible. if a mother is a carrier of an x-linked recessive disorder, her sons will be affected by the disease and her daughters will be carriers of the disease.
c. no, this isn't possible. x-linked recessive disorders can't "skip" generations like other genetic disorders.
d. yes, this is possible. males receive an x chromosome from their mother. if their mother is a carrier, the mutated x chromosome won't be passed on to sons and so they'll be unaffected.
13. what are the two main phases of the cell cycle?
a. prophase and anaphase
b. replication phase and recombination phase
c. multiplication phase and division phase
d. interphase and mitosis
14. what were the goals of the human genome project?
a. the goals of the human genome project were to sequence dna from 50 different species, including humans, and to understand the gene that causes cancer.
b. the goals of the human genome project were to sequence human dna and to identify all genes present in human dna.
c. the goals of the human genome project were to sequence human dna and to understand how it's damaged by exposure to toxins.
d. the goals of the human genome project were to sequence human dna and to identify the differences between human and chimpanzee dna.
15. the rearrangement of genetic information so that offspring can inherit new genetic combinations is called
a. recombination.
b. gene editing.
c. replication.
d. gene expression.
16. the central dogma of molecular biology is that dna is transcribed into mrna, which is then to protein.
a. transferred
b. translated
c. transduced
d. transformed
17. a three-letter sequence of mrna that encodes for a specific amino acid is called a/an a series of these links specific amino acids together to form a polypeptide.
a. encryption
b. codon
c. gene
d. dna
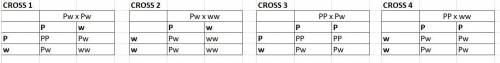
18. refer to the partially completed punnett square. purple flowers (p) are dominant to white flowers (w). what do you predict about the flower color of the offspring resulting from this cross?
a. about 25 percent of the offspring will have white flowers, and about 75 percent of the offspring will have purple flowers.
b. all of the offspring will have purple flowers.
c. about half of the offspring will have purple flowers, and about half of the offspring will have white flowers.
d. about 75 percent of the offspring will have purple flowers, and about 25 percent of the offspring will have white flowers.
19. cells can interact with other cells
a. that are nearby or within the same tissue.
b. nearby or throughout the body, depending on the type of cell-cell interaction.
c. during specific stages of the cell cycle.
d. that originated from the same stem cells.
20. (shown in firstpicture) refer to the figure showing a pedigree of a family affected by an x-linked recessive disorder. a female in generation 3 isn't a carrier of the disorder. how can this be?
a. females receive x chromosomes from their fathers only, which are unaffected in this case.
b. females don't have x chromosomes so aren't affected by gene disorders passed on the x chromosome.
c. females receive an x chromosome from each parent. if a mother is a carrier of an x-linked recessive disorder, her daughters have a 50 percent chance of receiving her normal x chromosome and a 50 percent chance of receiving her mutated x chromosome.
d. females receive an x chromosome from each parent, but in cases of recessive disorders, the mutated chromosome isn't passed on to daughters.

Answers: 3
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 22.06.2019 01:10, taylorwhitfield6
Which best describes meiosis? a. it produces cells that are identical to the original cell b. it is responsible for the replacement of damaged skin cells c. it is responsible for growth of the organism d. it produces male and female sex cells
Answers: 2


Biology, 22.06.2019 07:00, kaperry
Amale bird-of-paradise uses a dance to attract mates in which it flaps its tail feathers on the ground and jumps around a potential female mate. a different male bird-of-paradise does a similar dance but it jumps around the female in the opposite direction. the female bird is only attracted to one style of dance, in one direction.
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 08:20, barnhill6515
Which is not a characteristic of bacteria? a. they are unicellular. b. they are prokaryotic. c. they are the smallest form of life on earth. d. they are multicellular.
Answers: 2
Do you know the correct answer?
11. a red and a white snapdragon are crossed, and their offspring is pink. this is an example of
Questions in other subjects:

Mathematics, 24.03.2021 01:00


History, 24.03.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 24.03.2021 01:00

Advanced Placement (AP), 24.03.2021 01:00




Mathematics, 24.03.2021 01:00

Mathematics, 24.03.2021 01:00