Answers: 1
Other questions on the subject: Biology

Biology, 21.06.2019 22:00, chloerodgers56
An ecologist is studying the effects that a population of predators is having on a population of a prey. he used data from the field to produce this graph. which conclusion can draw from the graph?
Answers: 3

Biology, 21.06.2019 23:10, ErikHabdlowich
Drag the correct tiles to the image. not all tiles will be used. the diagram is a schematic representation of the electron transport mechanism in mitochondria. label the diagram to complete the model.
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 03:00, sophiav9780
Where does all the water go? according to the environmental protection agency (epa), in a typical wetland environment, 39% of the water is outflow; 46% is seepage; 7% evaporates; and 8% remains as water volume in the ecosystem (reference: united states environmental protection agency case studies report 832-r-93-005). chloride compounds as residuals from residential areas are a problem for wetlands. suppose that in a particular wetland environment the following concentrations (mg/l) of chloride compounds were found: outflow, 60.4; seepage, 73.7; remaining due to evaporation, 26.4; in the water volume, 46.8. (a) compute the weighted average of chlorine compound concentration (mg/l) for this ecological system. (round your answer to one decimal place.) mg/l (b) suppose the epa has established an average chlorine compound concentration target of no more than 58 mg/l. does this wetlands system meet the target standard for chlorine compound concentration? yes. the average chlorine compound concentration (mg/l) is too high. yes. the average chlorine compound concentration (mg/l) is lower than the target. no. the average chlorine compound concentration (mg/l) is lower than the target. no. the average chlorine compound concentration (mg/l) is too high.
Answers: 3

Biology, 22.06.2019 07:30, shelbellingswo
1. seamount a raised footwall block between normal fault creates this 2. syncline break between rocks where a hanging wall rises relative to a footwall 3. hot spring on rolling hills, this a dip between hills 4. volcanic neck created when a block with hanging walls slips down between normal faults 5. caldera underwater volcano that never reaches above sea level 6. horst natural hot water on earth's surface containing many minerals 7. graben underwater volcano whose top is eroded flat by waves 8. crater less than a mile in diameter; looks like a bowl at the top of a volcano 9. guyot magma that filled the central vent that remains after the volcano has eroded 10. reverse fault over 1 mile in diameter; looks like a bowl over a volcano
Answers: 3
Do you know the correct answer?
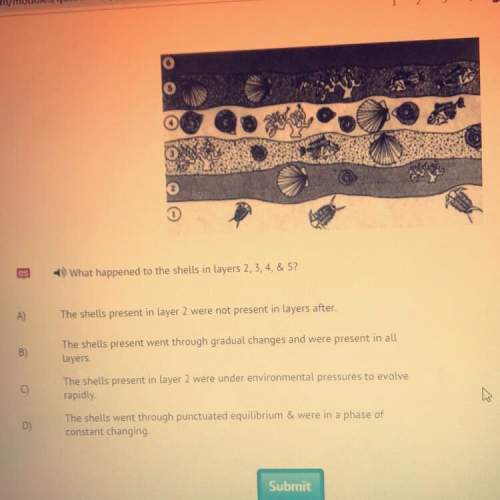
What happened to the shells in layers 2, 3, 4, & 5
...
...
Questions in other subjects:


History, 30.06.2019 10:30


History, 30.06.2019 10:30

Social Studies, 30.06.2019 10:30





Mathematics, 30.06.2019 10:30